Brain gliomas are malignant tumors that originate in the glial cells of the brain and can severely affect brain function.
Thanks to technological advances and specialized training of healthcare professionals, patients in Costa Rica now have access to state-of-the-art diagnostic and treatment options to combat this devastating disease.
But if you believe you might have this condition or have just received a diagnosis in that line, it is important to start by informing yourself.
What are Brain Gliomas?
As mentioned, brain gliomas are tumors that form in the glial cells of the brain. Glial cells are responsible for providing support and nourishment to neurons, as well as maintaining the structure of brain tissue.
Brain gliomas can be benign or malignant, and their severity depends on various factors, such as location and the type of glial cells involved.
These tumors can interfere with the brain’s electrical and chemical signals, leading to a wide variety of symptoms and complications. Early detection and appropriate treatment are crucial to improve the outlook for patients with brain gliomas.
Types of Brain Gliomas
There are several types of brain gliomas, each with distinctive characteristics and different degrees of malignancy. The most common types include astrocytic gliomas, oligodendrogliomas, and glioblastomas.
- Astrocytic gliomas originate in astrocytic cells, which play a crucial role in regulating the brain’s chemical balance.
- Oligodendrogliomas form in oligodendroglial cells, which are responsible for producing myelin, a substance that insulates and protects nerve fibers.
- Glioblastomas are the most aggressive brain gliomas and originate in immature astrocytic cells.
Each type of brain glioma has unique characteristics and requires a specific approach to diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms and Early Detection of Brain Gliomas
Brain gliomas can present a wide variety of symptoms, depending on their location and size.
Some of the most common symptoms include persistent headaches, changes in vision, difficulty speaking, and memory problems. However, these symptoms can also be indicative of other brain conditions, so it is crucial to undergo appropriate diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of a brain glioma.
Early detection of brain gliomas is crucial to ensure effective treatment and better outcomes for patients.
Diagnostic Procedures for Brain Gliomas
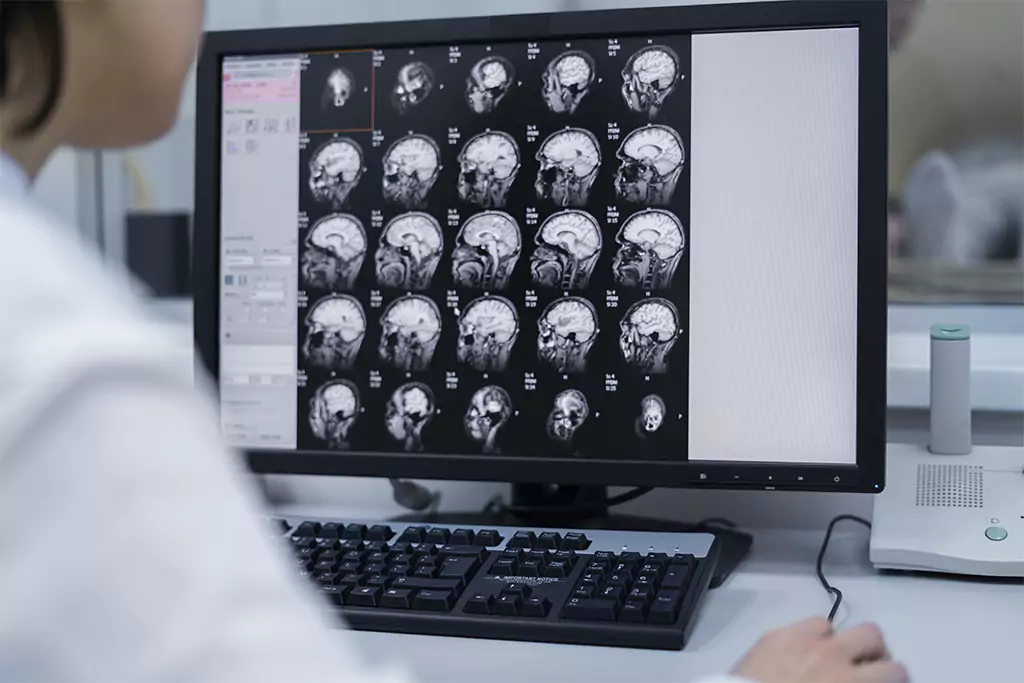
High-field magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the most commonly used techniques to diagnose brain gliomas. This technique uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the brain and detect the presence of tumors. MRI provides crucial information about the size, location, and extent of brain gliomas, which helps doctors plan the appropriate treatment.
Another commonly used diagnostic procedure is image-guided biopsy. During this procedure, a tissue sample from the tumor is taken using MRI images to guide the precise location of the biopsy.
This tissue sample is then examined in the laboratory to determine the exact type of brain glioma and its degree of malignancy.
Treatment Options for Brain Gliomas
Once a diagnosis of a brain glioma has been made, it is essential to determine the most appropriate treatment options for each patient.
In Costa Rica, it is possible to follow a comprehensive and multidisciplinary treatment approach that combines surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy to optimize outcomes.
Surgical Interventions for Brain Gliomas
Surgery is one of the fundamental pillars of brain glioma treatment. The goal of surgery is to remove as much tumor tissue as possible without damaging functional areas of the brain.
Specialists can now use intraoperative navigation and neurophysiological monitoring to ensure precise and safe surgery.

Intraoperative navigation
Uses preoperative MRI images to guide the surgeon during the operation and provide real-time information about the exact location of the tumor. This helps us identify the functional areas of the brain and avoid damaging them during tumor resection.

Neurophysiological monitoring
Records and evaluates the brain’s electrical responses to identify functional areas and ensure their preservation during tumor resection.
Radiotherapy for Brain Gliomas
Radiotherapy is another key component of brain glioma treatment. Radiotherapy uses high-energy radiation to destroy tumor cells and prevent their growth.
A patient with brain glioma may receive intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) or three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) to maximize precision and minimize side effects.
Radiotherapy is administered in daily sessions over several weeks, and the treatment plan is customized based on tumor characteristics and individual patient needs. Patients are closely monitored during treatment to assess effects and adjust the plan if necessary.
Chemotherapy for Brain Gliomas
Chemotherapy uses anticancer drugs to destroy tumor cells and prevent their growth. In the case of brain gliomas, chemotherapy is usually administered after surgery and radiotherapy to eliminate remaining tumor cells and prevent recurrence.
Contact me if you have any doubts about this topic, if you think you have brain gliomas, or if you have just received the diagnosis and want to get the best possible treatment. It will be a pleasure to advise you professionally and accompany you in recovering your quality of life.